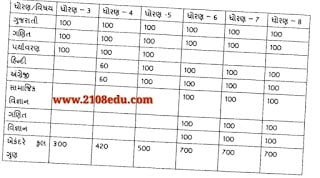
STD 1 to 8 MASS PRAMOTION PARINAM Patrk
Nidan Kasoti Mulyankan patrako std 3 to 8 mate all subjects pdf file useful for all teachers and school
JOIN US ON ” WHATSAPP” CLICK HERE
Ways to Deal with Risk
Life is risky, and insurance is not the only way to deal with risk. There are five basic ways to deal with risk. Think of the acronym STARR: Sharing – pooling the risk with a variety of other people who share the same risk. Transfer – such as buying insurance. Avoidance – removing the possible cause of a loss. Retention – keeping all or part of the financial risk of loss. Reduction – reducing the chance of loss with safety techniques.
In order for an insurance company to be able to accept premiums and pool money to pay for particular types of losses, the insurance company has to have a large enough number of similar risks. This is called the law of large numbers. This law makes it possible to statistically predict the probability of loss within the group, and therefore how much premium to charge. Ideally, insurable risk must meet certain criteria:
Losses to be insured must be definable
Losses must be accidental
Losses must be large enough to cause a hardship to the insured
There must be a homogeneous group of risks large enough to make losses predictable
(Law of large numbers)
Losses must not be catastrophic to many members of the group at the same time
The insurance company must be able to determine a reasonable cost for the insurance
The insurance company must be able to calculate the chance of loss
Nidan Kasoti Scanning std 3 to 8 Excel File
In addition, insurance can only pay money to people who have an insurable interest in the property lost. Insurable interest is any interest a person has in a possible subject of insurance, such as a car or home, of such a nature that if that property is damaged or lost, that person will suffer a real financial loss. For property and casualty insurance, the insurable interest must exist at the time the loss occurs.
Also, an insurance company must guard against the tendency of poorer than average risks to buy and maintain insurance. Adverse selection occurs when insureds select only those coverages that are most likely to have losses.
JOIN US ON ” WHATSAPP” CLICK HERE
Patrak A to F pdf Download Here